RNA Polymerase II Largest Subunit (RPB1)
For our studies of Polyporales we are sequencing the region between conserved domains A and C (approx. 1400 bp).
PCR Primers
| RPB1-Af | GAR TGY CCD GGD CAY TTY GG | Stiller and Hall, 1997 |
| RPB1-Cr | CCN GCD ATN TCR TTR TCC ATR TA | Matheny et al 2002 |
Alternatively the sequencing primer RPB1-Int2.2f (see below) gives very good results as a PCR primer when paired with RPB1-Cr (the product is approx. 400 bp shorter). This can be especially helpful if the PCR with Af and Cr fails or gives additional products and you want to avoid cloning.
Additional Sequencing Primers
| RPB1-Int2f | TTM BTC TRC TCG TTT YGC AC | Froslev et al 2005 |
| RPB1-Int2.1f | GCT GAA CGA GSA GTG C | Froslev et al 2005 |
| RPB1-Int2.2f | CGT TTT CGR TCG CTT GAT | Binder et al 2010 |
| RPB1-Int2.1r | GCA CTS CTC GYT CAG C | Froslev et al 2005 |
All “Int2” (also written as “i2”) primers bind at different points of Intron 2 (between domains A and B).
Usually you will only need one of the “Int2” forward primers to get the desired fragment.
Sequencing of the PCR product obtained with RPB1-Af- RPB1-Cr usually involves 4 primers: RPB1-Af, RPB1-Int2.2f, RPB1-Int2.1r, RPB1-Cr.
The primers RPB1-Int2f and RPB1-Int2.1f can be used as additional primers or alternatives to RPB1-Int2.2f if that primer fails.
If the PCR was done with RPB1-Int2.2f and RPB1-Cr you can use RPB1-Int2.1f as an additional sequencing primer to get a better overlap with RPB1-Cr.
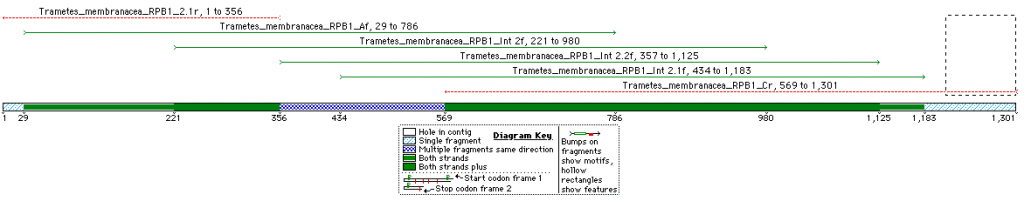
This is an overview of the expected fragment length and degree of overlap for the RPB1 sequence of Trametes membranacea (Click on image for a larger pic).
References
Binder, M.,K.H.Larsson, P.B. Matheny, and D.S.Hibbett. 2010. Amylocorticiales ord. nov. and Jaapiales ord. nov.: Early diverging clades of Agaricomycetidae dominated by corticioid forms. Mycologia, 102: 865-880
Frøslev, T. G., P. B. Matheny, and D. S. Hibbett. 2005. Lower level relationships in the mushroom genus Cortinarius (Basidiomycota, Agaricales): a comparison of RPB1, RPB2 and ITS phylogenies. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 37: 602-618.
Matheny, P.B., Liu, Y.J., Ammirati, J.F., and Hall, B.D. 2002. Using RPB1 sequences to improve phylogenetic inference among mushrooms (Inocybe, Agaricales). Am. J. Bot. 89: 688-698.
Stiller, J.W. and Hall, B.D. 1997. The origin of red algae: Implications for plastid evolution. PNAS 94: 4520 – 4525.
RNA Polymerase II Second Largest Subunit (RPB2)
For our studies of Polyporales we are sequencing the region between conserved domains 5 and 11 (approx. 2100 bp)
Important !! Two separate PCR are neccesary in you want to sequence the whole region between domains 5 and 11. However in many studies only the region between domains 5 and 7 is used. When working with very closely related taxa (e.g. species level taxonomy or closely related genera) the most variable region between domains 6 and 7 (approx. 700 bp) can be sequenced using RPB2-b6F and RPB2-b7.1R as PCR and sequencing primers.
Check also Brandon Matheny’s overview of RPB2
PCR Primers
PCR 1. Domains 5 – 7
| RPB2-f5F | GAY GAY MGW GAT CAY TTY GG | Liu et al. (1999) |
| RPB2-b7.1R | CCC ATR GCY TGY TTM CCC ATD GC | http://faculty.washington.edu/benhall/; Matheny (2005) |
Alternatives to b7.1R are:
| RPB2-b7R | GAY TGR TTR TGR TCR GGG AAV GG | http://faculty.washington.edu/benhall/; Matheny (2005) |
| RPB2-b7R2 | ACY TGR TTR TGR TCN GGR AAN GG | Matheny et al 2007 |
| RPB2-a8.0R | TCT CKG AAY TTV AGR TAY TCC AT | Binder et al 2010 |
Additional sequencing primers:
| RPB2-b6F | TGG GGY ATG GTN TGY CCY GC | http://faculty.washington.edu/benhall/; Matheny (2005) |
| RPB2-b6R2 | GGR CAN ACC ATN CCC CAR TG | Matheny et al 2007 |
Sequencing requires 4 primers in total, typically: RPB2-f5F, RPB2-b6F, RPB2-b6R2 and RPB2-b7.1R
PCR 2. Domains 7 – 11
| RPB2-b6.9F | TGG ACN CAY TGY GAR ATY CAY CC | Matheny et al 2007 |
| RPB2-b11R1 | TGG ATY TTG TCR TCC ACC AT | Matheny et al 2007 |
Alternatives to b11R1 are:
| RPB2-b10.9R | GTR AAS GGY GTG GCR TCY CC | http://faculty.washington.edu/benhall/ |
| RPB2-g11bR | CAA TCW CGY TCC ATY TCW CC | Liu et al. (1999) |
Additional sequencing primers:
| RPB2-f7cF | ATG GGY AAR CAA GCY ATG GG | Liu et al. (1999) |
| RPB2-b8.2R | CTN CGG AAN AGR CCR CGR TC | Matheny et al 2007 |
Sequencing requires 4 primers in total, typically: RPB2-b6.9F, RPB2-f7cF, RPB2-b8.2R and RPB2-b11R1
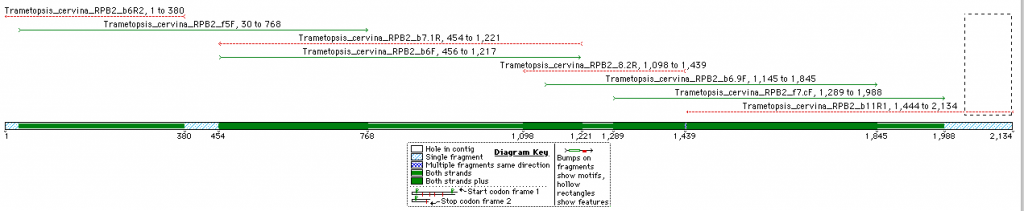
This is an overview of the expected fragment length and degree of overlap for the RPB2 sequence (Domains 5 -11) of Trametopsis cervina (Click on image for a larger pic).
References
Binder, M.,K.H.Larsson, P.B. Matheny, and D.S.Hibbett. 2010. Amylocorticiales ord. nov. and Jaapiales ord. nov.: Early diverging clades of Agaricomycetidae dominated by corticioid forms.Mycologia, 102: 865-880.
Liu, Y.L., Whelen, S., Hall, B.D., 1999. Phylogenetic relationships among ascomycetes: evidence from an RNA polymerase II subunit. Mol. Biol. Evol. 16, 1799–1808.
Matheny, P.B., 2005. Improving phylogenetic inference of mushrooms with RPB1 and RPB2 nucleotide sequences (Inocybe; Agaricales). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 35, 1–20.
Matheny, P. B., Z. Wang, M. Binder, J. M. Curtis, Y. W. Lim, R. H. Nilsson, K. W. Hughes, V. Hofstetter, J. F. Ammirati, C. Schoch, G. E. Langer, D. J. McLaughlin, A. W. Wilson, T. Frøslev, Z. W. Ge, R. W. Kerrigan, J. C. Slot, E. C. Vellinga, Z. L. Liang, T. J. Baroni, M. Fischer, K. Hosaka, K. Matsuura, M. T. Seidl, J. Vaura, and D. S. Hibbett. 2007. Contributions of rpb2 and tef1 to the phylogeny of mushrooms and allies (Basidiomycota, Fungi). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 43: 430-451.
Translation Elongation Factor 1-α (TEF1)
For our studies of Polyporales we are sequencing approx. 900-1200 bp of the gene
PCR Primers
| EF1-983F | GCY CCY GGH CAY CGT GAY TTY AT | Rehner and Buckley (2005) |
| EF1-2212R | CCR ACR GCR ACR GTY YGT CTC AT | Rehner and Buckley (2005) |
Alternative to EF1-2212R:
| EF1-2218R | ATG ACA CCR ACR GCR ACR GTY TG | Rehner and Buckley (2005) |
In our experience EF1-2212R works better than EF1-2218R as a PCR and sequencing primer.
Additional sequencing primers:
| EF1-1577F | CAR GAY GTB TAC AAG ATY GGT GG | Rehner and Buckley (2005) |
| EF1-1567R | ACH GTR CCR ATA CCA CCR ATC TT | Rehner and Buckley (2005) |
Sequencing requires 4 primers in total, typically: EF1-983F, EF1-1577F, EF1-1567R and EF1-2212R
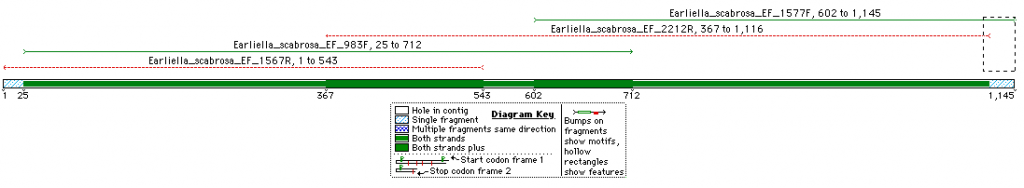
This is an overview of the expected fragment length and degree of overlap for the TEF1 sequence of Earliella scabrosa (Click on image for a larger pic).
References
Matheny, P. B., Z. Wang, M. Binder, J. M. Curtis, Y. W. Lim, R. H. Nilsson, K. W. Hughes, V. Hofstetter, J. F. Ammirati, C. Schoch, G. E. Langer, D. J. McLaughlin, A. W. Wilson, T. Frøslev, Z. W. Ge, R. W. Kerrigan, J. C. Slot, E. C. Vellinga, Z. L. Liang, T. J. Baroni, M. Fischer, K. Hosaka, K. Matsuura, M. T. Seidl, J. Vaura, and D. S. Hibbett. 2007. Contributions of rpb2 and tef1 to the phylogeny of mushrooms and allies (Basidiomycota, Fungi). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 43: 430-451.
Rehner, S.A., Buckley, E., 2005. A Beauveria phylogeny inferred from nuclear ITS and EF1-a sequences: evidence for cryptic diversification and links to Cordyceps teleomorphs. Mycologia 97, 84–98.
PCR protocol used for RPB1, RPB2 and TEF1
Protocol designed by Zheng Wang
1. 94 ˚C for 2:00
2. 94 ˚C for 0:40
3. 60 ˚C for 0:40
minus 1 ˚C per cycle
4. 72 ˚C for 2:00
5. Go to 2, 8 times
6. 94 ˚C for 0:45
7. 53 ˚C for 1:30
8. 72 ˚C for 2:00
9. Go to 6, 36 times
10. 72 ˚C for 10:00
11. 15 ˚C for ever
12. END